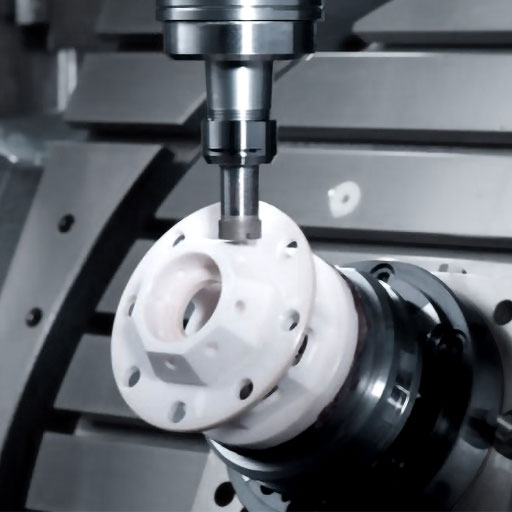
The strength and toughness of single crystal zirconia ceramics are based on its crystal structure. Because of its special crystal structure, it can be made into ceramic parts suitable for various harsh environments. Crystal structure.
There are three stable allotropes of zirconia: the monoclinic phase (m), the cubic phase (c), and the tetragonal phase (f)9. The monoclinic phase of pure zirconia is stable from room temperature to 1170 °C, above this temperature it transforms into tetragonal phase, and then transforms into cubic phase at 2370 °C until melting occurs at 2680 °C.
There is a hysteresis phenomenon when the ceramic bearing column changes from monoclinic phase to tetragonal phase. Upon cooling, the phase transition from t-phase to m-phase occurs in a temperature range of about 100°C below 1170°C. The transformation from t-phase to m-phase is a martensitic transformation, which causes a volume increase of about 3% to 4% upon cooling. This volume change is enough to exceed the elastic limit of ZrO2 grains and will cause cracking.
It is therefore difficult to manufacture large pure zirconia ceramic slab body materials. However, Harvie et al. (1975) proposed the use of this phase transition to improve the strength and toughness of zirconia ceramics. They believed that metastable tetragonal particles bound in a cubic matrix could be released from this restraint by a propagating crack. Causes a phase transition to the monoclinic phase.
Accompanied by the volume change of the martensite phase and the shear stress, the crack opening can be blocked, thereby increasing the resistance of the ceramic to crack propagation, that is, increasing the toughness of the ceramic. At the same time, it must be recognized that the presence of tetragonal zirconia particles in the cubic zirconia matrix causes several other reasons for the increase in primary and strength, including crack deflection (cracks are found in all two-phase ceramics) deflection), transformation toughening and crack toughening.
Pintejin machining ceramic service include : Alumina Ceramic Parts, Zirconia Ceramic, Silicon Carbide Ceramic, CNC Machined Aluminum Nitride Ceramic, Machinable Ceramic Parts, Glass Ceramic,Macor Ceramic,Powder Metallurgy Dies,Ceramic Injection Molding,Ceramic Dry Pressing,Ceramic Extrusion Dies




